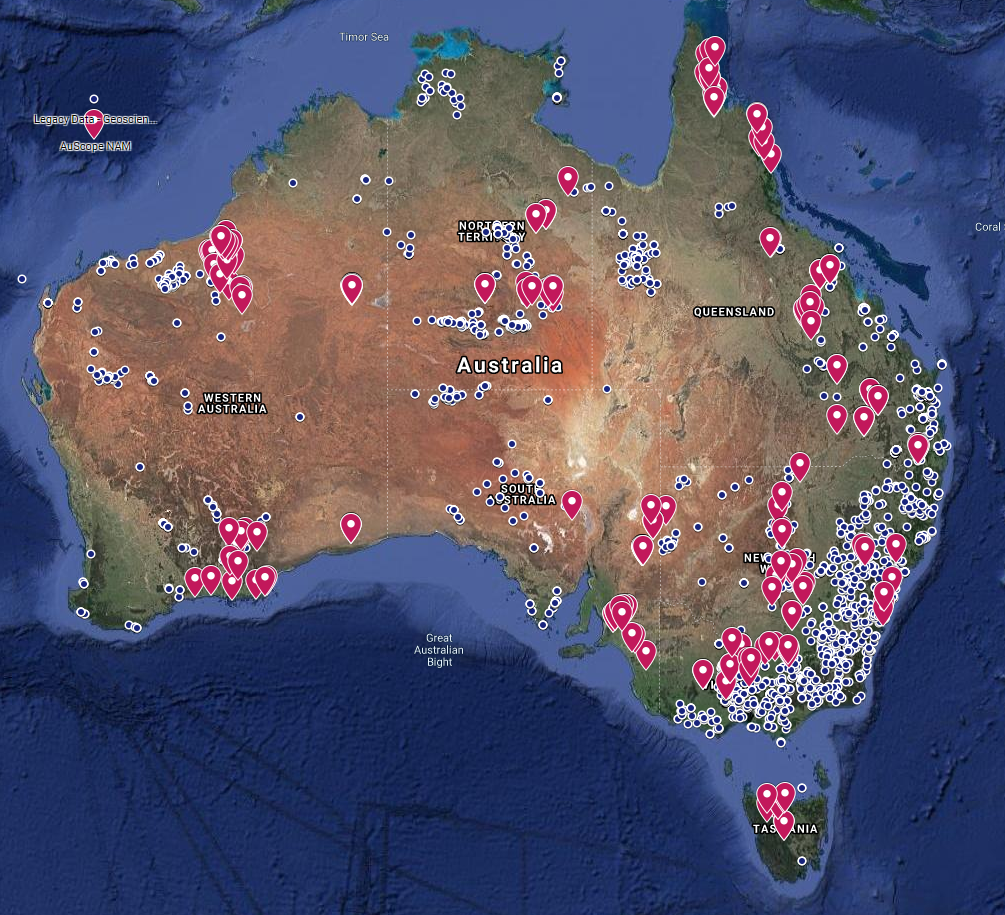
Expanding our knowledge of Australia’s geological ‘architecture’ and mineral potential: Extensions to the National Argon Map
Read MoreThe Mapping Australia’s Crust In Four Dimensions (MAC4D) project aimed to enhance ANU's SHRIMP-II age-mass spectrometer's capabilities, enabling the measurement of multiple isotopes crucial for mapping Australia's crust in four dimensions. This initiative helped facilitate the creation of integrated isotope-age maps, aiding in the discovery of new critical minerals.
Read MoreThis project aims to update outdated software across Ar-Ar laboratories in Australia to a unified open-source platform, enabling long-term accessibility, adaptability, and international compatibility.
Read MoreDevelopment of new dating methods will help push the boundaries of geochronology. Through the installation of a new laser system at Adelaide Microscopy, earth scientists can enhance their analyses of geological materials at an unprecedented rate, providing new temporal frameworks to resource exploration.
Read MoreGroundwater sampling will receive a boost through the combined effort of the CSIRO and University of Adelaide’s noble gas facilities to contribute to the development of the AusGeochem database and subsequent research in water security and industry sectors.
Read MoreAuScope is unlocking new insights into geological processes crucial for accumulating critical mineral deposits via revolutionising Sr-isotope micro-analysis in a range of geological materials using cutting-edge laser ablation multi-collector mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICP-MS).
Read MoreThe AGN+ project piloted the expansion of the AuScope Geochemistry Network (AGN) through the addition of several new university geochemistry analytical facilities to enhance accessibility to key geochemical data sets.
Read MoreSecuring advanced analytical technology for novel minerals exploration research
Read MoreThe Australian Atom Trap Trace Analysis (ATTA) is a state-of-the-art sovereign facility for measuring noble gas radioisotope concentrations better than parts per trillion. It enables the full understanding of groundwater systems, with a strong focus on provenance and residence time.
Read More